CSS align-content: Mastering Multi-Line Alignment in Flexbox & Grid
CSS Flexbox CSSGrid
Mastering align-content: A CSS Guide for Multi-Line Alignment
When working with CSS Flexbox or Grid Layout, you might encounter situations where your container has extra space in the cross-axis. While align-items controls the alignment of items along the cross-axis within each line, align-content steps in to manage the alignment of the lines themselves within the container. This is particularly useful when you have a multi-line flex container or a grid with multiple row tracks.
See the Pen Untitled by Anthony (@BuiltInOneDay) on CodePen.
Understanding align-content
align-content defines how the browser distributes space between and around lines of content along the flex container’s cross-axis (or grid container’s block axis). It only has an effect when there is more space in the cross-axis than needed to display the flex lines or grid tracks.
Key Differences: align-items vs. align-content
It’s crucial to distinguish align-items from align-content:
align-items: Aligns individual items within each flex line or grid area.align-content: Aligns the lines of flex items or the tracks of a grid as a whole within the container. Think ofalign-itemsas aligning items inside each row, andalign-contentas aligning the rows themselves within the container.
Common align-content Values
Let’s explore the most common values for align-content with examples:
flex-start (or start): Lines are packed at the start of the container.
CSS
.container {
display: flex; /* or display: grid; */
flex-wrap: wrap; /* For flexbox to create multiple lines */
`align-content: flex-start; /* or `align-content: start; */
height: 200px; /* Ensure container has extra space */
}HTML
<div class="container">
<div>Item 1</div>
<div>Item 2</div>
<div>Item 3</div>
<div>Item 4</div>
<div>Item 5</div>
</div>(In this example, all lines will be positioned at the top of the container.)
flex-end (or end): Lines are packed at the end of the container.
CSS
.container {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
align-content: flex-end; /* or align-content: end; */
height: 200px;
}(Lines will be positioned at the bottom of the container.)
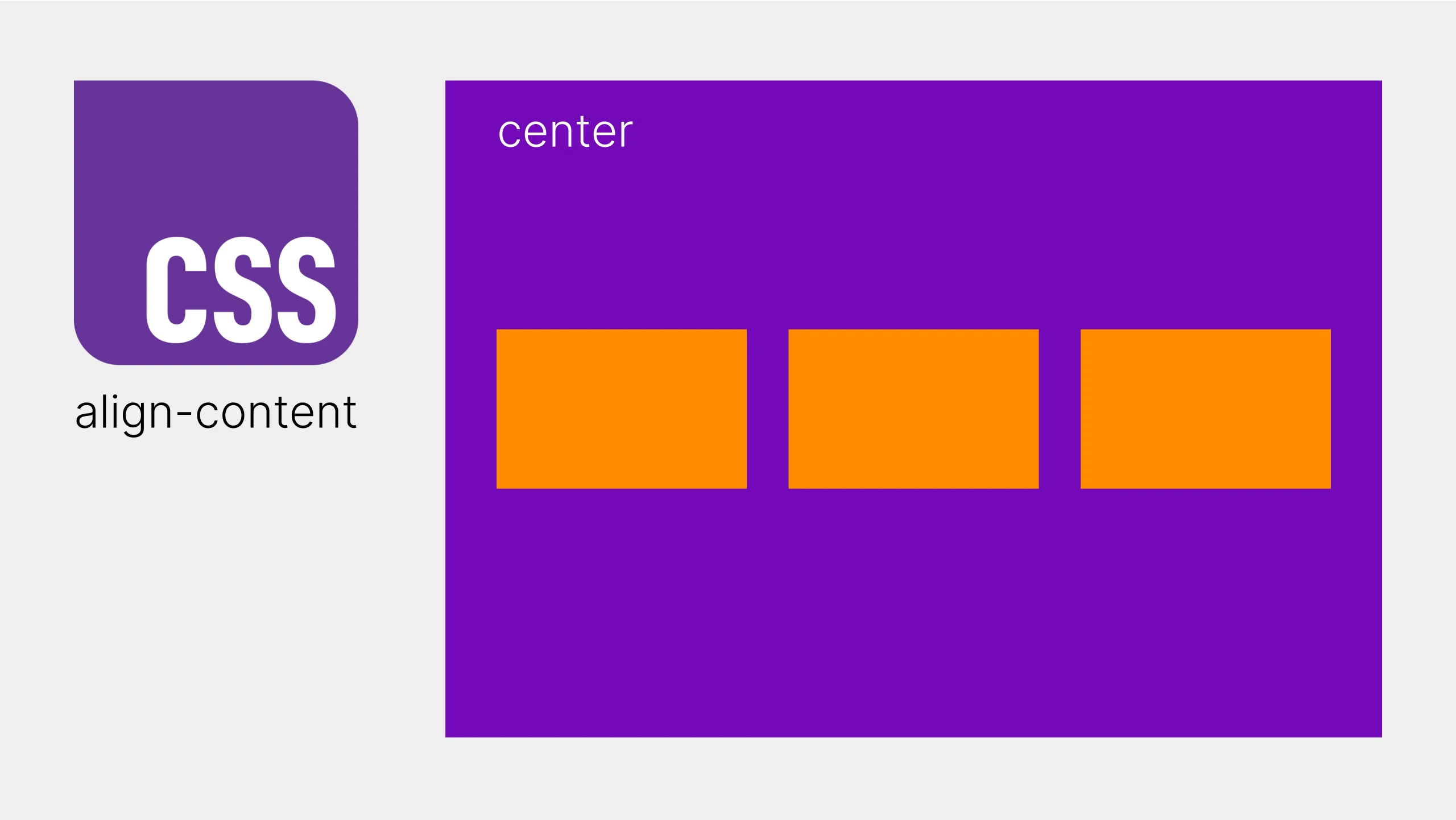
center: Lines are centered in the container.
CSS
.container {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
align-content: center;
height: 200px;
}(Lines will be vertically centered within the container.)
space-between: The first line is at the start, the last line is at the end, and remaining space is distributed evenly between the lines.
CSS
.container {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
align-content: space-between;
height: 200px;
}(Space is placed between the lines.)
space-around: Space is distributed evenly around each line, with equal space before the first line and after the last line.
CSS
.container {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
align-content: space-around;
height: 200px;
}(Space is placed around each line.)
stretch: Lines are stretched to fill the container. This is the default value.
CSS
.container {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
align-content: stretch; /* Default value */
height: 200px;
}(Lines will expand to fill the available height of the container, if possible.)
When to Use align-content
align-content is most effective when:
- Using Flexbox with
flex-wrap: wrap;or Grid Layout: It requires multiple lines or tracks to have something to align. - The container has extra space in the cross-axis: If the content already fills the cross-axis,
align-contentwon’t have a visible effect. - You need to control the distribution of space between lines/tracks: For example, to center a group of lines vertically or distribute them evenly within a container.
Conclusion
align-content is a valuable CSS property for fine-tuning the layout of multi-line flex containers and grid layouts. By understanding its different values and how it interacts with available space, you can achieve more sophisticated and visually appealing designs. Experiment with these values to see how align-content can enhance your layouts!
For more detailed information, refer to the MDN documentation on align-content.
Browser Support:
align-content in block layouts
Baseline 2024 newly available
Supported in Chrome: yes.
 Supported in Edge: yes.
Supported in Edge: yes.
 Supported in Firefox: yes.
Supported in Firefox: yes.
 Supported in Safari: yes.
Supported in Safari: yes.

Since April 2024 this feature works across the latest devices and browser versions. This feature might not work in older devices or browsers.